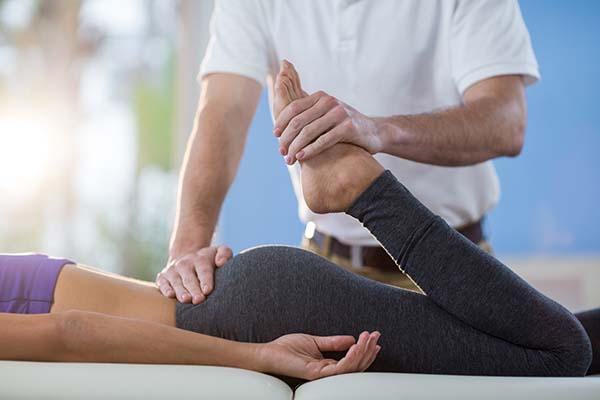
OT (occupational therapy) involves the use of assessment as well as intervention to maintain, recover, or develop the meaningful occupations, or activities, of communities, groups, or individuals. It’s an allied health profession that is performed by occupational therapists. Occupational therapists typically work with people who have impairments, injuries, disabilities, or health problems.
The AOTA (American Occupational Therapy Association) is the national professional association that represents the interests as well as concerns of OTs plus improves the quality of OT services. It defines occupational therapists as people who help individuals across their lifespan to take part in the things that they need and want to do, and this is through therapeutic use of daily activities (occupations).
The common occupation therapy interventions are helping kids with disabilities to fully take part in social situations and school, injury rehabilitation, as well as providing support for older people experiencing cognitive and physical changes.
 Occupational therapists are typically university-educated professionals, and they are required to pass a licensing exam for them to practice. OTs usually work closely together with professionals in medicine, clinical psychology, social work, nursing, audiology, speech therapy and physical therapy.
Occupational therapists are typically university-educated professionals, and they are required to pass a licensing exam for them to practice. OTs usually work closely together with professionals in medicine, clinical psychology, social work, nursing, audiology, speech therapy and physical therapy.
Working with Children
The occupations of children are centered around learning and playing. OTs work with kids with any condition, impairment or disability that affects their capability of performing the normal activities of life, like making friends, going to school, eating, getting dressed, as well as being part of a group or club. This includes the following:
- Sensory and attention issues
- Developmental delay and disabilities
- Physical disabilities (for instance, spina bifida)
- Acute medical, surgical plus orthopedic conditions
- Neurological conditions (for example, cerebral palsy)
Occupational therapists work in close cooperation with the child, his/her parents, and other people who are important in the child’s life, like their teacher, doctor, as well as other health professionals.
OTs can help kids achieve their developmental milestones like motor skills as well as hand-eye coordination for helping them with school, play, or independent skills such as throwing a ball, holding utensils or a pen). They can also educate and involve carers, parents, and other people to facilitate children’s development and learning. Occupational therapists can help children who have developmental delays learning everyday tasks.
Additionally, they can help children with behavioral issues maintain positive behaviors in all environments. For instance, instead of cutting out or hitting others, they can use positive methods to deal with anger like taking part in a physical activity or writing about it.
Acute Care
OTs work in inpatient hospital environments providing specialist interventions for individuals with different health conditions, including acute mental health, HIV, burns, falls, and post-surgery.
Acute care occupational therapists work to asses clients’ function, cognition, as well as psychosocial needs, plus they monitor client’s function plus progress, prescribing intervention and if it is necessary adaptive equipment for facilitating a safe and successful hospital discharge.
Mental Health
OTs in mental health use group and individual programs and activities in enhancing participation in the occupations of daily life – working, looking after oneself, and engaging in leisure as well as social pursuits. For instance, occupational therapists may work in partnership with consumers to develop particular strategies to allow participation in social activities.
Workplace Injury Management
An occupational therapist uses specialized assessments to determine functional necessities of different jobs, and the capacity of people to return to work. OTs can help with designing as well as coordinating graded programs of return to work. They can assist with educating employers and clients in safe work practices.
Also, they can help in modifying your work environment to accommodate the needs of people to prevent or minimize injuries plus ill-health. Additionally, they can work with individuals who have mental or physical needs in the workplace.
Rehabilitation and Independence
An occupational therapist work with individuals of all age groups to rehabilitate illness or injury. These rehabilitation areas include the following:
- Helping enhance or regain participation in the occupation of daily life after specific events like stroke, spinal injury or a hip replacement, or within a condition like multiple sclerosis or rheumatoid arthritis
- Prescribing and educating clients as well as carers in the adaptive equipment use to assist participation
- Assessing and modifying community and home environments to improve their independence and safety
- Ergonomic assessment as well as modification in the community, workplace, or home
- Providing or manufacturing splints after upper limb or hand injury
- As OTs work with both mental and physical health needs, they are well placed to provide a holistic approach that pays attention to physical needs and emotional wellbeing when they are working with people after illness or injury.
 There’s winter, spring, summer, fall, and of course my favorite season- Football!
There’s winter, spring, summer, fall, and of course my favorite season- Football!
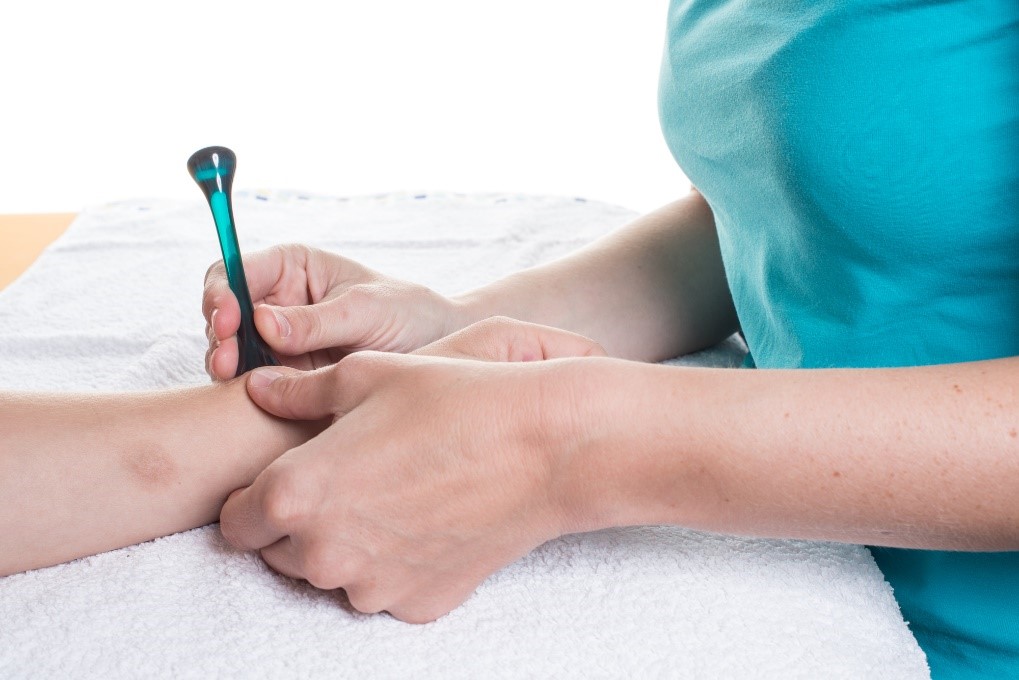
 American Occupational Therapy Associations say that
American Occupational Therapy Associations say that 
 PT, properly, you won’t need surgery. Not only will physical therapy help you eliminate the risk factor from happening, it will also help prevent any similar injuries in the future.
PT, properly, you won’t need surgery. Not only will physical therapy help you eliminate the risk factor from happening, it will also help prevent any similar injuries in the future.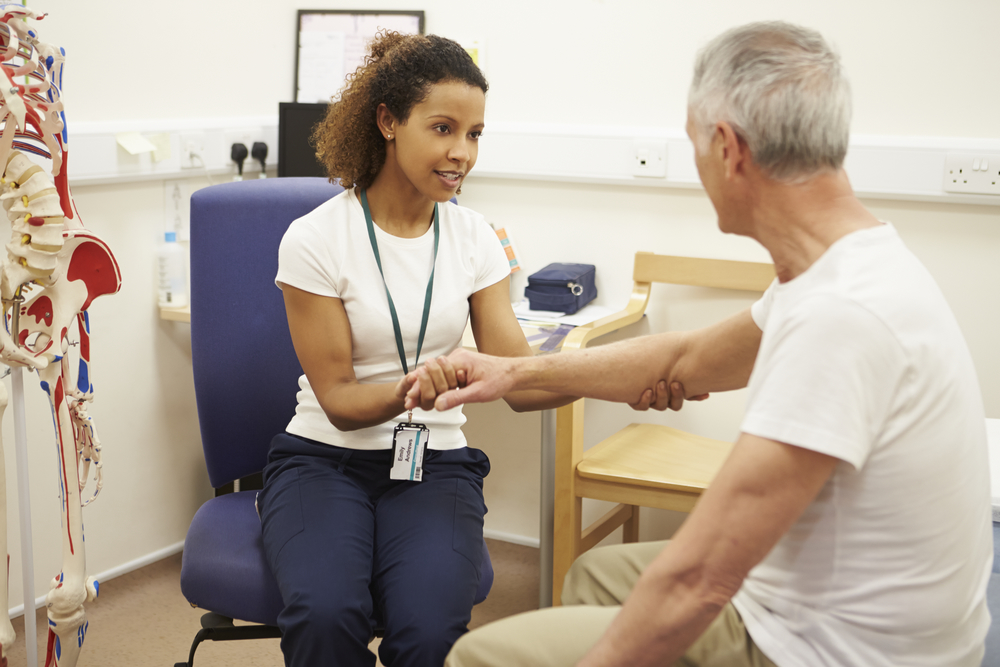
 A physical therapist evaluates the patient and comes up with a treatment program tailored to the needs of the patient. Emphasis is placed on patient education and training to ensure that the patient becomes independent as soon as possible. Treatment outcomes are evaluated as program implementation progresses.
A physical therapist evaluates the patient and comes up with a treatment program tailored to the needs of the patient. Emphasis is placed on patient education and training to ensure that the patient becomes independent as soon as possible. Treatment outcomes are evaluated as program implementation progresses.
 Occupational therapists are typically university-educated professionals, and they are required to pass a licensing exam for them to practice. OTs usually work closely together with professionals in medicine, clinical psychology, social work, nursing, audiology, speech therapy and physical therapy.
Occupational therapists are typically university-educated professionals, and they are required to pass a licensing exam for them to practice. OTs usually work closely together with professionals in medicine, clinical psychology, social work, nursing, audiology, speech therapy and physical therapy.